So, you're weighing your options between forex and options trading. The choice really comes down to one core difference: In forex, you're directly buying and selling currency pairs. With options, you're trading contracts that give you the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price.
Your decision hinges on what you're more comfortable with. Are you drawn to the fast-paced, high-leverage world of global currencies? Or do you prefer the strategic, defined-risk framework of derivatives?
Forex vs. Options: A Quick Comparison for Traders
When you first step into the financial markets, one of the biggest forks in the road is choosing between forex and options. These two arenas offer completely different ways to pursue profits, each with its own mechanics, risk profiles, and strategic demands. Getting a solid grasp on these differences is the first real step toward finding the market that fits your trading style.
Forex trading is a global, decentralized market that happens over-the-counter (OTC). It’s an absolute giant in terms of liquidity, running 24 hours a day, five days a week, and it’s all about the relative value of one currency against another.
Options, on the other hand, are standardized contracts you'll find on centralized exchanges. They aren't limited to currencies; they cover a huge range of assets like stocks, indices, and commodities. Crucially, they come with fixed expiration dates and strike prices, which adds a layer of complexity.
Key Market Characteristics
The data tells a big part of the story. The infographic below zeroes in on the critical differences in leverage, trading volume, and costs that really define the day-to-day experience in each market.
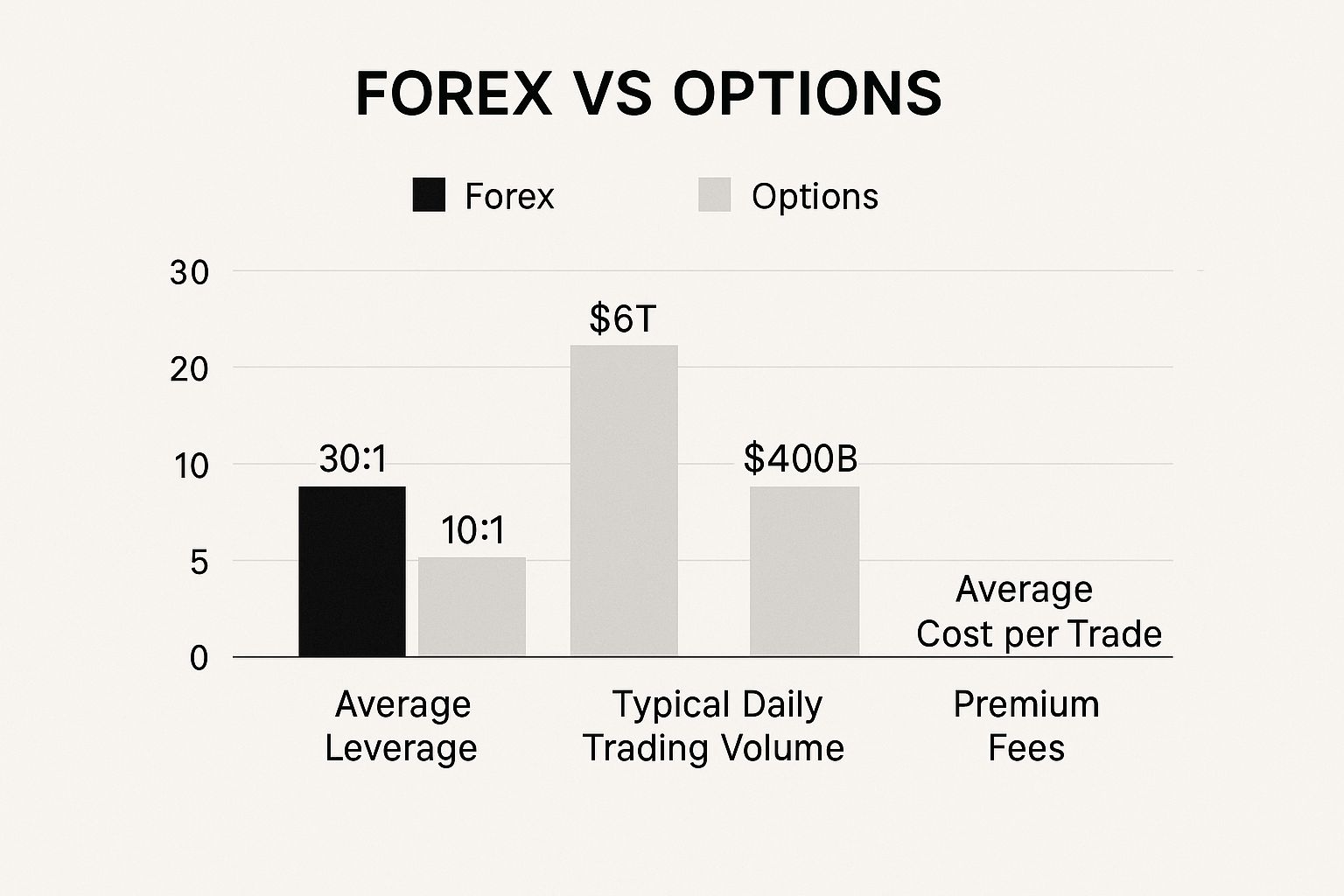
As you can see, forex dominates in daily volume and available leverage, which has a massive impact on liquidity and how efficiently you can use your capital. To get an even more granular look at how these two stack up, check out our complete guide on options vs forex trading strategies.
For a quick, at-a-glance reference, this table breaks down the foundational differences.
Core Differences Between Forex and Options
This table provides a foundational summary of the key characteristics that distinguish the forex and options markets for traders.
| Characteristic | Forex Trading | Options Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Traded | Directly trading currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD). | Buying/selling contracts for an underlying asset. |
| Market Structure | Decentralized, Over-the-Counter (OTC). | Centralized and traded on public exchanges. |
| Trading Mechanism | Speculating on currency price movements (pips). | Speculating on price, volatility, and time decay. |
| Ownership | You own the underlying currency position. | You own a contract, not the underlying asset. |
This initial look should give you a clearer picture of the two landscapes. It's the starting point for a deeper dive, helping you figure out which environment is the right fit for your financial goals and your personal comfort with risk.
Understanding Core Market Mechanics

To really get to grips with the forex vs. options debate, you have to look under the hood at how each market actually works. Their core mechanics are what shape everything—from when you can trade to the kinds of opportunities you'll find. Forex and options aren't just different; they practically operate in separate financial universes.
The forex market is a sprawling, decentralized web. There's no central building or physical floor; instead, it's an over-the-counter (OTC) market where transactions happen directly between banks, major financial players, and individual traders worldwide. This global network is why it can run 24 hours a day, five days a week, creating a market that’s always in motion.
The Forex Market Structure
The decentralized nature of forex is really its defining trait. Think of it less like the New York Stock Exchange and more like a massive, interconnected computer network spanning the globe. This setup is what allows for its incredible scale and constant activity.
- Global and Continuous: Trading literally follows the sun, starting in Sydney, then moving to Tokyo, London, and finally New York. This handoff means there's almost always an active session somewhere.
- High Liquidity: With so many participants trading at once, it's typically very easy to get in and out of a trade without the price jumping around too much.
This constant flow means forex traders need to be prepared to react to economic news and global events at any hour.
The sheer size of this market is hard to wrap your head around. The forex market is the largest in the world, with an average daily trading volume that tops $6.6 trillion. To put that in perspective, the entire global options market, while significant, trades closer to $300 billion daily. This liquidity gap is a big reason why forex traders often see tighter spreads and faster order fills. You can dig deeper into these market differences in this comparison of forex and options trading.
The Options Market Structure
Options trading, on the other hand, plays by a completely different set of rules. Unlike the OTC world of forex, options are standardized contracts that trade on centralized, regulated exchanges, such as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). This structure brings a formal set of rules and defined parameters that govern every trade.
Each options contract is built on a few key elements:
- Strike Price: The set price at which you can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The specific date when the contract becomes worthless.
- Premium: The cost you pay to buy the options contract itself.
This regulated, time-sensitive environment makes for a much more structured trading experience. Instead of the endless flow of forex, options trading revolves around specific contracts with a clear start and finish. Your entire strategy is locked within the contract's expiration date, making timing and volatility analysis absolutely critical for every single trade. This fundamental difference in structure is the most important thing to consider when deciding which market is right for you.
Analyzing Your Risk and Profit Potential

When it comes to forex versus options, the way you handle risk and map out your potential profits couldn't be more different. Your final decision will likely come down to what you can stomach in terms of risk and what kind of profit opportunities you're looking for. Each market has its own distinct structure and tools that shape your outcomes.
In the forex market, profit potential is all about leverage. By controlling a large amount of currency with a relatively small deposit, even the smallest price fluctuations, called pips, can translate into significant gains. A well-timed trade can produce impressive returns on your margin.
Of course, that same leverage is a classic double-edged sword. Just as it magnifies your profits, it can amplify your losses. A sudden, unexpected price swing against your position can wipe out your initial deposit and then some. This creates a scenario of theoretically unlimited risk, which is why disciplined risk management isn't just a good idea—it's essential for survival.
The Defined Risk of Options Trading
Options trading, especially if you're a buyer, is built on a completely different risk foundation. When you buy an option, whether it's a call or a put, your maximum risk is locked in from the very start. The most you can ever lose is the premium you paid for the contract.
Your maximum possible loss when buying an option is 100% defined and limited to the premium you paid to acquire it. This provides a huge psychological edge and a hard stop on risk, getting rid of the fear of a single trade causing a catastrophic account blow-up.
This built-in safety net allows traders to speculate on volatile assets without the kind of open-ended exposure you find in leveraged markets like forex. You know your worst-case scenario before you ever hit the "buy" button. To get a better handle on these concepts, it's worth exploring these essential trading risk management techniques that can be applied in any market.
Non-Linear Profit Scenarios
Another game-changing difference is how profits are made. Forex gains are linear and straightforward; a 50-pip move in your favor results in a fixed, predictable profit. Options, on the other hand, offer non-linear profit potential. This means your gains aren't just tied to which way the price moves.
Options traders have more tools in their belt to profit from market behavior. The "Greeks," a set of variables that influence an option's price, unlock some sophisticated strategies:
- Volatility (Vega): You can build a trade that profits from a rise or fall in market volatility, even if the underlying asset's price doesn't move much.
- Time Decay (Theta): Some strategies are designed to earn money simply as time passes and an option's value erodes, a tactic that works beautifully in flat or sideways markets.
This multi-dimensional aspect allows for a much more creative and nuanced trading approach. For example, if you think an asset will jump 1%, a forex trader profits directly from that move. An options trader, however, could see their contract value multiply exponentially, benefiting from both the price change and an accompanying spike in implied volatility. The result can be a far larger return on the initial investment.
Comparing Strategic Depth and Complexity
When you're weighing forex against options, you're not just choosing between two different assets. You're actually picking from two completely different strategic toolkits. The way you approach one market simply won't work in the other.
At its core, forex trading is all about directional conviction. Options, on the other hand, open up a world of strategic possibilities that go far beyond a simple "up or down" bet.
The Directional Focus of Forex
The strategic game in forex is refreshingly direct. You use technical indicators and fundamental news to form a bias—is the EUR/USD going up or down?—and then you put your money where your analysis is.
Most forex strategies, while different in timeframe, share this same DNA:
- Scalping: Quick in-and-out trades that aim to capture tiny price fluctuations, often lasting just minutes.
- Day Trading: All positions are opened and closed within the same day, so you're flat overnight.
- Swing Trading: Holding positions for several days or even weeks to ride a larger market wave.
In every case, the goal is linear. If the price moves your way, you profit. If it moves against you, you lose. It's a straightforward, two-dimensional playing field.
The Multi-Faceted World of Options Strategies
This is where things get interesting. Options trading introduces layers of strategic depth that leave simple directional bets behind. An option's value isn't just tied to price; it's also heavily influenced by time and volatility. This lets you build trades that can profit even if the market goes nowhere.
Options let you build a trade around a precise market theory. You can construct positions that make money if a stock stays flat, gets more volatile, or even just as time ticks by. This is a total game-changer for a strategic trader.
The modern retail forex market exploded to its $6.6 trillion daily volume on the back of the internet and deregulation. Options trading, which was formalized with the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 1973, has a smaller daily footprint but makes up for it in strategic firepower. You have access to a whole playbook of structures like spreads, straddles, and iron condors that just don't have a parallel in spot forex. For a closer look at these market differences, check out this deep dive into forex and options markets.
This complexity means you can tailor a strategy to a very specific forecast. For example, an "iron condor" is a popular options play designed to profit if a stock's price stays within a defined range by expiration. You don't need to guess the direction—just that it will remain stable. This requires a different way of thinking and a much deeper understanding of all the moving parts. Tracking how these complex strategies actually pan out is crucial, and reviewing your own trading performance metrics is the only way to know if your approach is truly working.
How Leverage and Capital Requirements Differ

When you look at forex vs. options, you'll see that how you use your money and get access to leverage are worlds apart. These differences are not just minor details; they fundamentally shape your risk exposure and how much cash you need to get started, so it's a critical piece of the puzzle.
In forex, leverage is a tool your broker gives you—it's essentially a short-term loan to boost your trading power. A common leverage ratio is 50:1, which means for every $1 of your own money, you can command $50 in the market. This is how forex traders can open big positions with a relatively small account, turning tiny currency fluctuations into meaningful profits.
Of course, that power is a double-edged sword. A small price move against you gets magnified just as quickly, leading to substantial losses. If your losses eat into your capital too much, your broker issues a margin call. This forces you to either add more money to your account immediately or have your trades automatically closed for a loss. This open-ended risk is the classic trade-off of forex leverage.
The Built-In Leverage of Options
Options approach leverage from a completely different angle. It’s not something you borrow; it’s baked right into the structure of the financial instrument itself. You pay a relatively small fee, called a premium, to control a much larger amount of an underlying asset.
Here's a practical example. A standard stock option contract lets you control 100 shares. If a stock is trading at $150, buying 100 shares directly would set you back a cool $15,000. In contrast, an option contract to control those very same shares might only cost you a premium of a few hundred dollars.
The most crucial distinction is that an option buyer's risk is strictly limited to the premium paid. Once you buy the contract, you cannot lose more than that initial investment, completely eliminating the risk of margin calls and catastrophic losses.
This structure gives you a powerful, built-in risk management advantage. You get the upside of controlling a large position without the unlimited downside that haunts highly-leveraged forex trades. It's this defined-risk nature that makes options so attractive to many traders. While forex might offer bigger leverage numbers on paper, options give you a much safer and more predictable way to manage your capital on every single trade.
Which Trading Style Best Suits Your Goals?
So, forex or options? There’s no simple "winner" here. The right choice comes down to you—your personality, how much risk you’re comfortable with, and what you’re trying to accomplish as a trader. Think of it less as a contest and more as a matching process.
For those just starting out, the forex market is often the path of least resistance. It's incredibly liquid, open 24/5, and you don't need a massive amount of capital to get in the game. If you want to trade based on major economic news and use leverage to magnify small price moves, forex is the most direct way to do it. The mechanics are relatively straightforward: you're betting on whether a currency will go up or down.
On the other hand, if you’re the kind of person who enjoys a good puzzle and wants to build sophisticated trades with strictly defined risk, options offer a far more intricate and rewarding experience. It’s a market built for strategists.
An options trader isn't just betting on direction. They're crafting a specific thesis about an asset's future. You can build positions that profit from a stock staying flat, from a spike in volatility, or from the simple passage of time—a level of strategic depth you just won't find in spot forex.
Finding Your Fit: Two Trader Profiles
To figure out where you belong, take an honest look at which of these descriptions sounds more like you. This is the single most important step.
The Forex Trader Profile
Forex traders tend to be direct and action-oriented. They thrive on the pace and simplicity of the currency markets.
Does this sound familiar?
- You prefer simplicity. You want to focus purely on price direction—up or down—without worrying about extra variables like time decay or implied volatility.
- You value high liquidity. Being able to get in and out of a trade instantly with minimal slippage is a priority, especially with major currency pairs.
- You're comfortable with high leverage. You understand and accept the risks that come with using significant leverage to amplify your potential returns from small price changes.
- You're an active trader. You enjoy the fast-paced, around-the-clock nature of the market and want to react to global news as it happens.
The Options Trader Profile
In contrast, an options trader is more of a planner. They embrace complexity because it gives them more control and more ways to win.
See if this resonates with you:
- You're strategic and analytical. You enjoy digging into the "Greeks"—like theta (time decay) and vega (volatility)—to build a truly nuanced position.
- You demand defined risk. Knowing your absolute maximum loss before you place a trade isn't just a preference; it's a requirement.
- You want flexibility. You want to build strategies that can profit whether the market is trending up, down, sideways, or just plain volatile.
- You're patient and methodical. You're okay with working within expiration dates, giving your strategy the time it needs to play out.
Ultimately, the best market for you is the one that feels like a natural extension of your own strengths. Forex offers a focused, high-speed experience. Options provide a sophisticated framework for precision, control, and strategic trading.
Answering Your Top Questions About Forex and Options
When you're weighing forex against options, a few key questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle them head-on to clear up any confusion and give you the confidence to decide which market fits your style.
Can You Trade Forex Using Options?
Absolutely. This is done with a specific type of derivative called a forex option.
Think of it as a hybrid. A forex option gives you the right—but not the requirement—to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price before a specific date. This approach blends the defined-risk nature of options with the massive scale of the currency market. It's a powerful way to speculate on where you think an exchange rate is headed, often focusing on volatility itself rather than just the direction of the move.
Which Market Is Better for Short-Term Trading?
Both markets are hotspots for short-term traders, but they serve different strategies. The forex market is king for scalping and day trading. Its incredible liquidity and 24-hour access mean you can jump in and out of trades on tiny price shifts with minimal friction.
Options are also great for short-term plays, especially around specific events like an earnings report. You might buy a weekly option to catch a quick move. However, your success isn't just about getting the direction right. You're also fighting against time decay and shifts in volatility, which adds layers of complexity.
For pure, high-frequency directional bets, the forex market’s tight spreads and always-on nature usually win out. But if you're looking to make a calculated, event-driven trade with a capped downside, short-term options are hard to beat.
What Are the Typical Costs in Forex vs. Options Trading?
The cost structures are fundamentally different.
In forex, your main cost is baked right into the trade: the spread. This is just the tiny difference between the buying and selling price of a currency pair. Some brokers might add a small commission on top of that, but the spread is the primary fee.
Options trading costs are more explicit and have a few moving parts:
- The Premium: The upfront cash you pay to buy the option contract.
- Commissions: Most brokers charge a fee for each contract you trade.
- Assignment/Exercise Fees: If you decide to exercise your option, you'll likely face an additional fee for the service.
So, while forex costs are integrated, options costs are itemized. You see exactly what you're paying for each component of the trade.
Ready to apply professional-grade analytics to your trading? OTC Charts MT4 provides the real-time, precise data you need to master the markets. Integrate our advanced charting tools with your Pocket Option account and make every decision with confidence. Get started today at OTC Charts MT4.


