When you boil down the forex vs options trading debate, the core difference is simple. In forex, you're directly buying and selling currencies, trying to profit as their values move. With options, you're buying the right—but not the requirement—to buy or sell an asset at a set price later on. This distinction gives options a ton of strategic flexibility.
So, the right choice for you really depends on what you're after. Do you prefer making straightforward bets on market direction, or do you want to build more complex trades with clearly defined risks?
Choosing Your Path in Trading
Before you get lost in charts and indicators, let's get one thing straight: there's no single "better" market. The right fit comes down to your personality, how much capital you have, what kind of risk you can stomach, and your ultimate financial goals. This guide is designed to cut through the jargon and give you a clear framework to start with.
Understanding the Core Appeal
Forex trading drops you right into the world's biggest financial market. Here, your job is to speculate on the ever-changing values of currency pairs. It’s a perfect playground for traders who get a kick out of following macroeconomic news, interest rate decisions, and geopolitical events that shape entire economies.
Options trading, on the other hand, offers a different kind of leverage—strategic power. You aren't just betting on whether a price goes up or down. You can construct trades that profit from the passage of time (time decay), big swings in volatility, or even when the market goes nowhere. For many, the ability to control an asset with a predefined risk is a massive advantage.
Key Takeaway: Here’s a good way to think about it. Forex trading is like a high-speed F1 race where you’re betting on which car (currency) will beat another. Options trading is more like a chess match, where every move (strategy) is carefully calculated to control the board, no matter what happens.
A First Look at Key Differences
To make a smart choice, it helps to see how these two markets stack up on the basics. This initial comparison lays the groundwork for the more detailed analysis to come, helping you see where your own style might naturally lean.
The table below gives you a quick, high-level overview of the main distinctions between forex and options trading.
| Feature | Forex Trading | Options Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Traded | Currency Pairs (e.g., EUR/USD) | Contracts on underlying assets (e.g., stocks, ETFs) |
| Primary Goal | Profit from the change in exchange rates | Profit from price, time, or volatility changes |
| Market Access | Decentralized, 24/5 global market | Centralized exchanges with fixed hours |
| Risk Profile | Potentially unlimited risk due to leverage | Risk limited to the premium paid (for buyers) |
This comparison immediately brings the fundamental trade-offs into focus. Forex gives you incredible liquidity and round-the-clock market access, which is a huge draw for active, short-term traders. Options provide a more structured arena with a massive toolbox of strategies, appealing to those who prefer to make calculated, multi-faceted plays. As we dig deeper into how each market works, these differences will become even more apparent, guiding you toward the path that best suits your trading ambitions.
How Market Structure and Liquidity Shape Your Trades

Knowing where you trade is just as crucial as deciding what to trade. The forex and options markets are built on entirely different foundations. These structural differences directly affect everything from your market access and trading hours to the very opportunities you'll encounter.
The foreign exchange market is a sprawling, decentralized network. It's not anchored to a single building but operates through a global web of banks, brokers, and massive financial institutions. This is precisely why it can run 24 hours a day, five days a week, seamlessly passing the baton from one major financial center to the next as the sun moves across the globe.
For traders juggling a day job or those who prefer to trade during specific high-volume periods, like the London-New York overlap, this around-the-clock access is a game-changer.
The Impact of Liquidity
The immense scale of the forex market means one thing: incredible liquidity. With roughly $6.6 trillion changing hands every day, it completely dwarfs the options market's estimated $300+ billion daily volume. This massive flow of cash ensures that for major pairs like the EUR/USD or USD/JPY, there's almost always a buyer for every seller. The result? Tight bid-ask spreads and near-instant trade execution. You can get a deeper dive into these market distinctions at Pocket Option's blog.
Options, on the other hand, are traded in a centralized, exchange-based environment. When you buy or sell an option, you're doing it on a specific, regulated exchange like the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) or through the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
This centralized model means trading is restricted to official exchange hours, which usually align with a standard business day in that region. Once the closing bell rings, trading halts. You simply have to wait for the market to reopen to manage your positions.
Key Differentiator: Forex is a decentralized, 24/5 playground fueled by interbank liquidity. Options operate within the structured, time-bound world of centralized exchanges, where liquidity is concentrated in a public order book.
How Structure Influences Your Strategy
These fundamental realities have a direct impact on the strategies you can effectively deploy and how you manage risk.
- Forex Trading: The high liquidity and 24-hour cycle are perfect for short-term approaches like scalping and day trading. News from anywhere in the world can spark instant volatility, creating a constant stream of opportunities. For example, a surprise economic announcement from Japan can be traded immediately, even if it's 2 AM in New York.
- Options Trading: The exchange-based structure offers a different kind of stability. Prices are listed transparently in a central order book, meaning every participant sees the same quotes. The fixed hours also mean you can step away without the same level of anxiety about overnight gaps that a forex trader might feel from activity in foreign sessions.
Ultimately, the choice in the forex vs options trading debate often boils down to this structural preference. Do you want the fluid, always-on nature of a global, decentralized market? Or do you prefer the organized, clock-in-clock-out environment of a centralized exchange? Your answer will point you toward the right path.
Comparing Core Trading Mechanics Side-by-Side
When you pit forex against options, you're really looking at two fundamentally different ways to approach the markets. The very mechanics of how you place a trade, handle risk, and take profit are worlds apart. It's not just a matter of preference; it's about choosing a framework that aligns with your entire trading philosophy.
This image gives a great visual snapshot of the difference. On one side, you have the straightforward price chart of forex. On the other, the structured payoff diagram of an option.
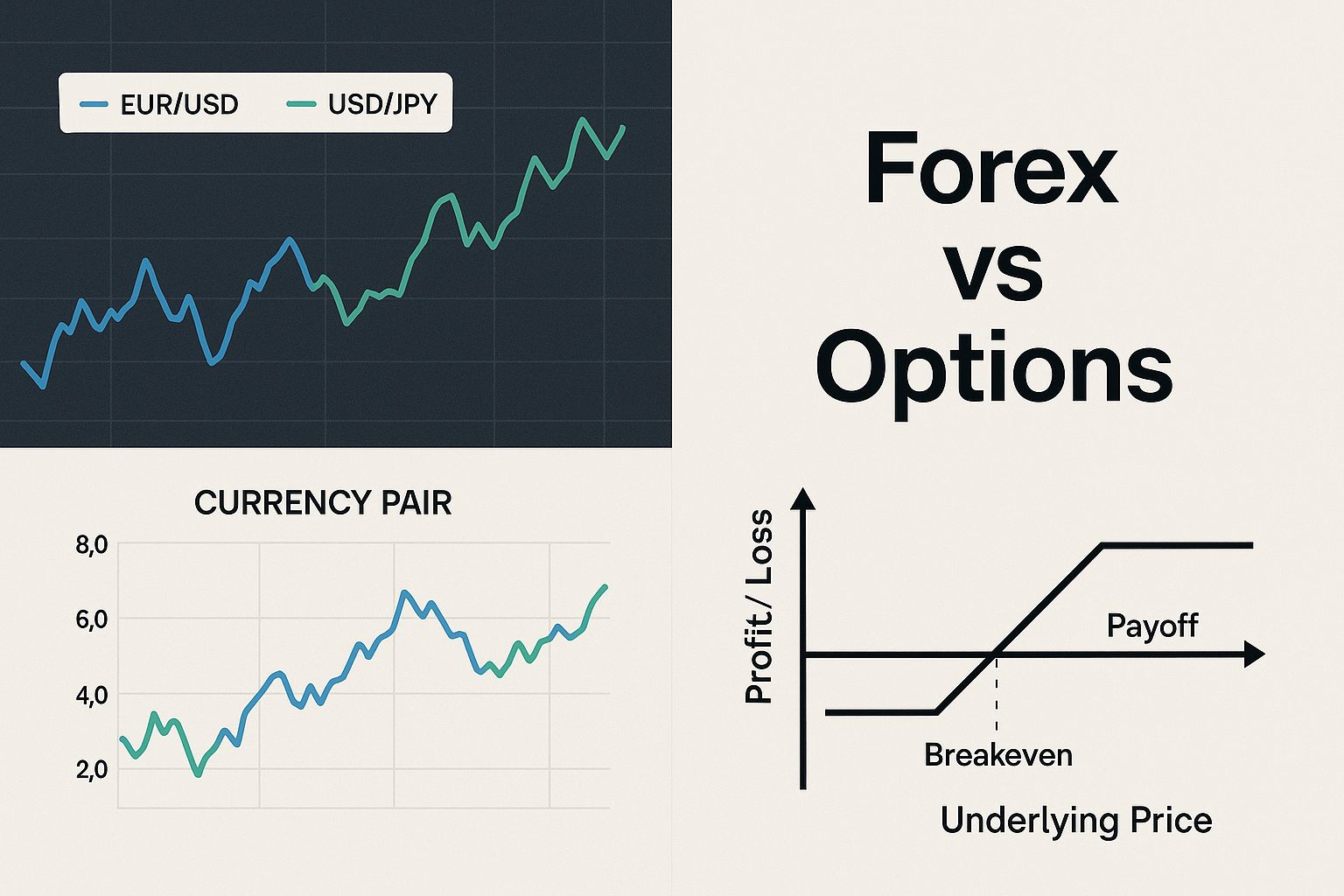
You can see the difference immediately: forex is about tracking price movement, while options are about crafting a specific outcome.
H3: Leverage: A Tool vs. An Inherent Feature
Both forex and options offer leverage, but they deliver it in completely different ways.
In the forex world, leverage is a tool handed to you by your broker—essentially, a short-term loan. It lets you command a much larger position than your account balance would normally allow. For example, with 50:1 leverage, your $1,000 deposit could control a $50,000 position. This is a classic double-edged sword; it can amplify your wins but just as easily magnify your losses.
Options, on the other hand, have leverage baked right into their DNA. When you buy an options contract, you pay a small premium for the right to control a significant amount of the underlying asset (usually 100 shares of stock). There’s no loan involved. The leverage is an intrinsic part of the product.
Key Insight: Forex leverage is an external tool from your broker that amplifies your market exposure. Options leverage is an inherent benefit of the contract, giving you control over an asset for a fraction of its price without taking on debt.
H3: Deconstructing the Risk Profile
The way risk is managed is probably the single biggest difference between these two.
When you buy an option, your risk is capped from the moment you enter the trade. The absolute most you can lose is the premium you paid for that contract. If you're wrong, the option expires worthless, and that's it. Your loss is defined and limited.
Forex is a different beast entirely. A leveraged forex trade carries the risk of losses that can blow past your initial deposit. A sudden market spike against you could lead to a margin call or, in a worst-case scenario, wipe out your account if you aren't disciplined with your stop-loss orders. While your profit potential is technically unlimited, so is your risk without tight controls.
This is a critical distinction. If you value a built-in safety net and clearly defined risk, buying options is hard to beat. If you're confident in your ability to manage risk actively with tools like stop-losses, the direct exposure of forex might be more your speed.
H3: The Profit Playbook: From Direction to Dimensions
So, how do you actually make money? The answer reveals the strategic depth each market offers.
Forex trading is almost entirely a directional game. You profit when you correctly predict where a currency pair is headed. You go long on the EUR/USD because you believe the Euro will rise against the Dollar, or you go short because you think it will fall. It’s a pure play on price movement.
Options trading, however, opens up a playbook with multiple dimensions. Yes, you can make simple directional bets, but you can also profit from other market dynamics:
- Time Decay (Theta): You can sell options and profit as their time value trickles away each day, even if the underlying asset’s price stands perfectly still.
- Implied Volatility (Vega): You can build trades designed to profit from a rise or fall in expected market choppiness, completely independent of price direction.
- Price (Delta): This is your classic directional bet, but it comes with the nuance of how an option's price changes in relation to the underlying asset.
If you want to dig deeper into these strategies, our dedicated article on option trading vs forex breaks them down in much greater detail. This ability to isolate and trade different market variables is what gives options their reputation for strategic flexibility.
To make this crystal clear, here’s a straightforward breakdown of how the core mechanics stack up.
Forex vs Options Trading Core Mechanics
The table below contrasts the fundamental workings of each trading style, showing how they differ at the most basic level.
| Mechanic | Forex Trading | Options Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Control | Direct ownership of a currency position. | Right to buy/sell an underlying asset. |
| Leverage Source | Provided by the broker (e.g., 30:1, 100:1). | Inherent in the contract (premium controls a larger asset value). |
| Risk for Buyers | Potentially unlimited; can exceed initial capital. | Defined and limited to the premium paid. |
| Profit Drivers | Almost exclusively price direction. | Price direction, time decay, and volatility changes. |
Ultimately, this isn't just a choice between two products. It's a choice about what kind of trader you are. Do you want to be a pure directional speculator focused on price action? Or are you a strategist who enjoys building complex plays based on multiple market factors? Your answer will point you in the right direction.
Navigating Volatility and Strategic Complexity
Volatility is the pulse of the market, but the way forex and options traders engage with it couldn't be more different. This is where we move beyond simple mechanics and really get into the strategic heart of the forex vs. options debate.
A forex trader looks at a volatile market and asks a direct question: "Where is the price headed?" Their job is to get on the right side of that move. An options trader, facing the same chaos, asks something different: "How can I profit from this volatility itself, even if I’m not sure about the direction?"
Volatility: Market Engine vs. Tradable Asset
In the forex world, volatility is the direct result of real-world events. A surprise interest rate decision, a geopolitical flare-up, or a shocking jobs report can send currency pairs on a wild ride. Forex traders react to this, trying to capitalize on the price swings by taking a directional stance. It's a classic approach: predict the direction correctly and your profit is tied to how far the price moves.
Options trading introduces a whole new layer: implied volatility (IV). This isn't just a measure of past price swings; it's the market's collective guess on how much an asset's price will move in the future. IV is baked directly into an option's premium. When IV is high, options get more expensive. When it’s low, they get cheaper. This creates an entirely separate playground for traders.
An options trader can build a position that profits solely from a spike or collapse in implied volatility, with little to no movement in the underlying asset's price. That kind of strategic angle simply doesn't exist in forex.
Real-World Scenario: A Surprise Interest Rate Hike
Let's ground this in a practical example. Imagine a central bank unexpectedly raises interest rates.
-
The Forex Trader's Play: The textbook forex move is to immediately buy that country's currency. If the U.S. Federal Reserve hikes, a trader might buy the USD/JPY, betting the dollar will strengthen. Success is linear—it depends entirely on that currency pair going up. It's a clean, directional bet.
-
The Options Trader's Play: An options trader looking at a related asset, like an S&P 500 ETF, has a much wider playbook. They could execute a long straddle by buying both a call and a put option at the same strike price. This position doesn't care about direction; it profits from a massive price move either up or down, directly capitalizing on the explosion of uncertainty.
Or, if they believe the market’s panic is overblown, they could do the opposite: sell expensive options to collect the rich premium, betting that the high implied volatility will soon settle back down. This is where options reveal their strategic depth.
Strategic Depth and Layers of Complexity
This brings us to one of the most important distinctions in the forex vs. options discussion. While successful forex trading demands incredible skill, the strategies themselves are structurally straightforward. They center on entries, exits, stop-losses, and take-profits, all based on price action.
Options, on the other hand, can be as simple as a single directional bet or as complex as a multi-legged structure designed for a very specific market outcome. They allow you to build positions based on:
- Direction: Simple long calls (bullish) or puts (bearish).
- Volatility: Straddles and strangles that profit from big moves.
- Time: Selling options to profit from time decay (theta).
- Range-Bound Markets: Iron condors that make money if the market stays flat.
Historically, forex has been defined by its massive global scale and sensitivity to economic shifts. The 2008 financial crisis, for instance, created epic volatility, with major currency pairs swinging 10%-20% in days. Options volatility is more tied to the specific underlying asset and its time until expiration. You can learn more about how traders turn these dynamics into unique strategies at BrokersView.
A Practical Look at Costs and Capital
Every trade has its price, and getting a handle on these costs is the only way to figure out what you're actually earning. The cost structures in forex and options trading are fundamentally different, and this difference directly impacts how much money you need to get started and what it takes to turn a profit.
In the forex world, your main cost is the bid-ask spread. Think of it as a tiny built-in fee—the difference between the buying and selling price for a currency pair. On major pairs like the EUR/USD, liquidity is so deep that this spread can be incredibly tight, keeping your transaction costs low. The only other common fee is the overnight swap fee, which is a small charge (or sometimes a credit) you get for holding a trade open after the market closes.
Options trading plays by a different set of rules. Here, the big cost is the premium, which is the price you pay upfront to buy the options contract. On top of that, your broker will usually charge a commission for each contract you trade, and you might see some small exchange or regulatory fees tacked on as well.
Crucial Insight: Forex costs are mostly invisible, baked right into the spread. Options costs are explicit—you pay a premium and commissions upfront. This isn't just a minor detail; it completely changes how you calculate your break-even point for every single trade.
Capital Requirements and Getting in the Door
There’s a common myth that you need a fortune to start trading. While having more capital certainly helps, the barrier to entry for forex and options is worlds apart.
Forex is famous for being one of the easiest markets to get into. You can find plenty of reputable brokers who will let you open an account with as little as $100. Thanks to micro-lots, you can trade with incredibly small position sizes, making it a great testing ground for traders who are just starting out with limited funds.
Buying options, on the other hand, can demand more cash upfront, particularly if you’re eyeing high-priced stocks. The premium for a single options contract on a company like Tesla or Amazon could easily run you several hundred, if not thousands, of dollars. Even though your risk is capped at what you paid for the premium, the initial investment can be much steeper than a small forex position.
For instance, you might pay a $1,000 premium to control 100 shares of a $200 stock with an option. To control a similar-sized position in the forex market, you'd need a much smaller deposit because of the high leverage brokers offer.
How Costs Set Your Breakeven Point
This is where the rubber meets the road. Your costs dictate how much the market has to move in your favor before you even start to make money.
- For a Forex Trader: Your breakeven point is simply the spread. If the spread on EUR/USD is 1 pip, the price only needs to tick 1 pip in your direction to put you in the green.
- For an Options Buyer: Your breakeven is much further out. It’s the strike price plus the premium you paid and any commissions. The underlying stock has to make a pretty significant move just to cover your initial cost before you start seeing any profit.
This reality is why forex is so popular for scalping and other strategies that aim for small, frequent wins. For options traders, the higher initial cost means you’re usually hunting for bigger, more explosive price moves to make the trade worthwhile.
Finding the Right Market for Your Trading Profile
https://www.youtube.com/embed/ZX-Tp4zgJYc
Choosing between forex and options trading isn’t about which market is "better"—it's about finding out which market is better for you. Your personality, how much time you can commit, and your stomach for risk are what really matter. Let’s move past the textbook definitions and look at how to match a market to your real-world trading style.
To make this practical, we'll look at three common trader archetypes. By seeing what they need and the challenges they face, you'll probably see a bit of yourself in one of them, which makes the choice much clearer.
The High-Frequency Day Trader
This trader lives for the action. Their entire game is built around getting in and out of the market multiple times a day, trying to skim profits from tiny, rapid price moves. To pull this off, they need a market that’s always on, incredibly liquid, and has razor-thin spreads to keep trading costs from eating up their gains.
For this person, forex is the clear winner. The market runs 24 hours a day, five days a week, so there’s always an opportunity somewhere in the world. More importantly, its colossal liquidity—we're talking trillions of dollars a day—keeps spreads on major currency pairs extremely tight. That’s absolutely critical for any strategy that depends on bagging small, repetitive profits.
Options just aren't built for this. Their fixed exchange hours and typically wider bid-ask spreads create too much friction for high-frequency scalping. The cost structure and pace simply don't align with the rapid-fire approach this trader needs to survive.
Recommendation: If your strategy is all about active, short-term trading from sunup to sundown, the constant access and low costs of the forex market create the perfect playground.
The Part-Time Speculator
This is someone with a full-time job who wants to trade on the side. They can't be glued to a screen all day, but they can dedicate a few hours each week to research and place a few well-planned trades. What they need most is a market that offers clearly defined risk and strategic depth without demanding constant babysitting.
This is where options trading really shines. Its most powerful feature is defined risk. When you buy an option, the absolute most you can ever lose is the premium you paid to open the position. That peace of mind is gold for someone who can't watch every little price tick.
On top of that, options offer strategies that go way beyond just betting on direction. A part-time trader can structure a trade to profit from a big news event, a jump in volatility, or even if the market just goes sideways—all while knowing their maximum loss upfront. This flexibility lets them build trades that fit their schedule and risk comfort level perfectly. Our detailed breakdown of the forex vs options dynamic explores these strategic differences further.
The Strategic Portfolio Hedger
This person is more of an investor than a pure trader. Their main goal isn't just to speculate; it's to protect their existing portfolio of stocks and other assets from a potential market crash. They think in longer time horizons and need a precise tool to manage risk across all their holdings.
For this job, options are unequivocally the superior tool. Hedging is one of the core reasons options were invented in the first place. An investor can buy put options on an index ETF (like the SPY) to act as an insurance policy for their entire stock portfolio. If the market tanks, the profits from their put options will help cushion the blow from their falling stock values.
Forex trading just doesn't have this kind of surgical, asset-specific hedging power. Sure, you could short a currency as a broad bet against an economy, but that's a blunt instrument. It lacks the precision needed to protect a specific stock or an index. For sophisticated risk management, nothing in the forex world comes close to what options can do.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're trying to decide between trading forex and options, a few common questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle them head-on, drawing from real-world trading experience to clear up any confusion.
Which Is Better for Beginners?
For someone just starting out, forex is generally the more straightforward path. At its core, you're just deciding whether a currency pair will go up or down. The platforms are typically intuitive, and you can get your feet wet with a very small account—sometimes as little as $100—which is perfect for learning without risking a lot of capital.
Options, on the other hand, have a much steeper learning curve. You’re not just betting on direction; you also have to master concepts like time decay, implied volatility, and strike prices. While the fixed risk of buying an option is appealing, the strategic depth can feel like a lot to handle when you're still just trying to figure out how markets move.
Can You Trade Both Forex and Options?
Of course. In fact, many seasoned traders use both. It's not about picking one and sticking with it forever; it's about having a versatile toolkit. You might use a forex trade for a quick, directional play on the Euro, while simultaneously using options to set up a longer-term position or hedge your stock portfolio.
The real shift in thinking happens when you stop seeing it as an "either/or" decision. Think of it as adding more tools to your workshop. One market might be your go-to, but the other can be incredibly useful for specific situations, ultimately making you a more well-rounded trader.
What Are the Main Risks in Each Market?
This is a crucial point because the risk profiles couldn't be more different. It’s one of the biggest factors in the forex vs options trading debate.
- Forex Risk: The main danger here is leverage. It's fantastic when a trade goes your way, but it's just as powerful in the other direction. A sharp move against your position, without a proper stop-loss, can lead to losses that wipe out more than just your initial deposit.
- Options Risk: As an options buyer, your risk is capped. The absolute most you can lose is the premium you paid for the contract. That’s it. For options sellers, however, the story changes completely—the risk can be significant, and in some cases, theoretically unlimited.
For a deeper dive, you can learn more by exploring our complete guide on options vs forex trading.
Which Market Is More Profitable?
There's no magic answer here. Neither market is guaranteed to be "more profitable." Your success comes down to your strategy, discipline, risk management, and how well you can read the market at any given time. A skilled forex day trader can build a great track record, just as a savvy options strategist can.
A better question to ask yourself is: "Which market's profit model fits my strengths?" If you're good at predicting simple price direction, forex is a direct way to capitalize on that. But if you have a knack for analyzing volatility or understanding how time impacts an asset's price, options give you far more ways to structure a winning trade.
Ready to elevate your binary options trading on Pocket Option? OTC Charts MT4 provides advanced, real-time over-the-counter charting tools directly within MetaTrader 4, giving you the professional-grade accuracy needed to anticipate market movements. Get the competitive edge with OTC Charts MT4 today.


