Embarking on a trading journey without a solid plan to manage risk is like navigating a storm without a rudder. While the allure of high returns is powerful, the reality is that long-term success hinges not on a few spectacular wins, but on consistent capital preservation. This is where mastering trading risk management techniques becomes non-negotiable. Ignoring risk doesn't just expose you to potential losses; it guarantees them over time, eroding both your capital and your confidence. Effective risk management is the bedrock of a sustainable trading career, transforming speculative gambles into calculated, strategic decisions.
This guide moves beyond theoretical concepts to provide a practical, actionable framework for protecting your portfolio. We will dissect seven essential techniques, from foundational principles like position sizing and stop-loss orders to more advanced strategies like portfolio heat management and volatility adjustments. Each section is designed to be a clear, concise blueprint, offering specific implementation steps, particularly for traders utilizing the robust charting capabilities of OTC Charts on MT4. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive toolkit to not only survive market volatility but to thrive within it, ensuring you stay in the game long enough to achieve your financial goals.
1. Position Sizing
Position sizing is arguably the most critical of all trading risk management techniques. It’s not about predicting the market; it’s about controlling your exposure so that no single trade can inflict catastrophic damage on your portfolio. This technique determines the appropriate number of units to trade based on your account size, risk tolerance, and the specific risk of the trade, defined by your stop-loss distance.

Pioneered by figures like Van K. Tharp and Ralph Vince, position sizing is the secret weapon of professional traders. Legendary hedge fund manager Paul Tudor Jones famously limits his risk on any single idea to just 1-2% of his total capital. This principle ensures longevity in the markets, allowing a trader to withstand a string of losses without blowing up their account. It shifts the focus from "Will this trade be a winner?" to "How much can I afford to lose if I'm wrong?"
How to Implement Position Sizing
The core idea is to risk a small, fixed percentage of your account on every trade. A common and prudent rule is the 1% rule.
Here’s the simple calculation:
- Determine Your Risk Amount: Account Size x Risk Percentage (e.g., $10,000 x 1% = $100).
- Define Your Trade Risk: Entry Price – Stop-Loss Price (for a long trade).
- Calculate Position Size: Risk Amount / Trade Risk per Share/Unit.
For instance, if you have a $10,000 account and want to risk 1%, your maximum loss per trade is $100. If you’re buying a stock at $50 with a stop-loss at $48, your risk per share is $2. Your position size would be $100 / $2 = 50 shares. This systematic approach is a cornerstone of effective trading risk management techniques.
Key Insight: Proper position sizing decouples your trading decisions from emotional impulses like fear and greed. By pre-defining your maximum loss, you can execute your strategy with discipline, knowing that the outcome of any individual trade is mathematically insignificant to your long-term survival.
2. Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order is a cornerstone of disciplined trading, acting as an automated exit plan to cap potential losses. It is a pre-set order placed with a broker to sell a security when it reaches a specific price. This technique serves as an essential safety net, ensuring that a losing trade doesn't spiral out of control and protecting your capital from significant drawdowns. It effectively removes emotional, in-the-moment decision-making from the process of taking a loss.

The concept has been a staple for legendary traders for over a century. Early 20th-century trader Jesse Livermore used "mental stops," while modern pioneers like William O'Neil built the 7-8% stop-loss rule directly into his famous CANSLIM system for growth stocks. The renowned Turtle Traders, a group part of a famous trading experiment, used volatility-based stops calculated with the Average True Range (ATR) to navigate trending markets. This widespread adoption underscores its importance as one of the most fundamental trading risk management techniques.
How to Implement Stop-Loss Orders
The key is to place stops at logical technical levels rather than arbitrary percentages. A well-placed stop should be at a price point that, if breached, invalidates your original trading thesis.
Here are a few practical tips for setting effective stops:
- Use Technical Levels: Place stops just below key support levels for long trades or just above key resistance levels for short trades.
- Consider Volatility: Use the Average True Range (ATR) to set a stop that accounts for the asset's normal price fluctuations, preventing you from being stopped out by market noise.
- Trailing Stops: For winning trades, a trailing stop can be used to lock in profits. It automatically moves up as the price rises but stays in place if the price falls, securing gains while giving the trade room to grow.
Failing to use a stop-loss is one of the most common trading mistakes to avoid. Learn more about common trading pitfalls and how to steer clear of them.
Key Insight: A stop-loss is not a sign of expecting to fail; it's a plan for what to do if a trade doesn't work out. It defines your maximum pain point before you enter a position, allowing you to trade with objectivity and preserve your capital to trade another day.
3. Diversification
Diversification is the classic adage of not putting all your eggs in one basket, adapted for the financial markets. It is one of the most fundamental trading risk management techniques, involving the strategic allocation of capital across various assets, markets, strategies, or even timeframes. The goal is to smooth out returns and reduce the impact of poor performance in any single area on your overall portfolio. By combining assets that react differently to the same economic events, you can mitigate unsystematic risk.
Pioneered in a formal sense by Nobel laureate Harry Markowitz through Modern Portfolio Theory, diversification is a principle championed by institutional giants. Ray Dalio's "All Weather" portfolio is a masterclass in diversifying across economic environments, not just asset classes. Similarly, David Swensen’s revolutionary Yale Model heavily relies on diversifying into alternative assets. This approach protects a portfolio from the isolated shocks that can cripple a concentrated account.
How to Implement Diversification
Effective diversification goes beyond simply buying different stocks. It requires a thoughtful approach to correlation, ensuring the assets you hold are genuinely independent of one another. For traders, this can mean diversifying across different currency pairs, commodities, indices, and even trading strategies (e.g., combining a trend-following strategy with a mean-reversion one).
Here are key principles to apply:
- Asset Class Diversification: Spread your capital across different classes like forex, commodities (gold, oil), and indices (S&P 500, FTSE 100). These often have low or negative correlations.
- Strategy Diversification: Don't rely on a single setup. A market that is unfavorable for your primary trend-following strategy might be perfect for a range-bound or breakout strategy.
- Geographic Diversification: Invest in different economic regions. A downturn in the US market might not affect Asian or European markets in the same way.
The infographic below summarizes the core objectives of a well-diversified trading portfolio.
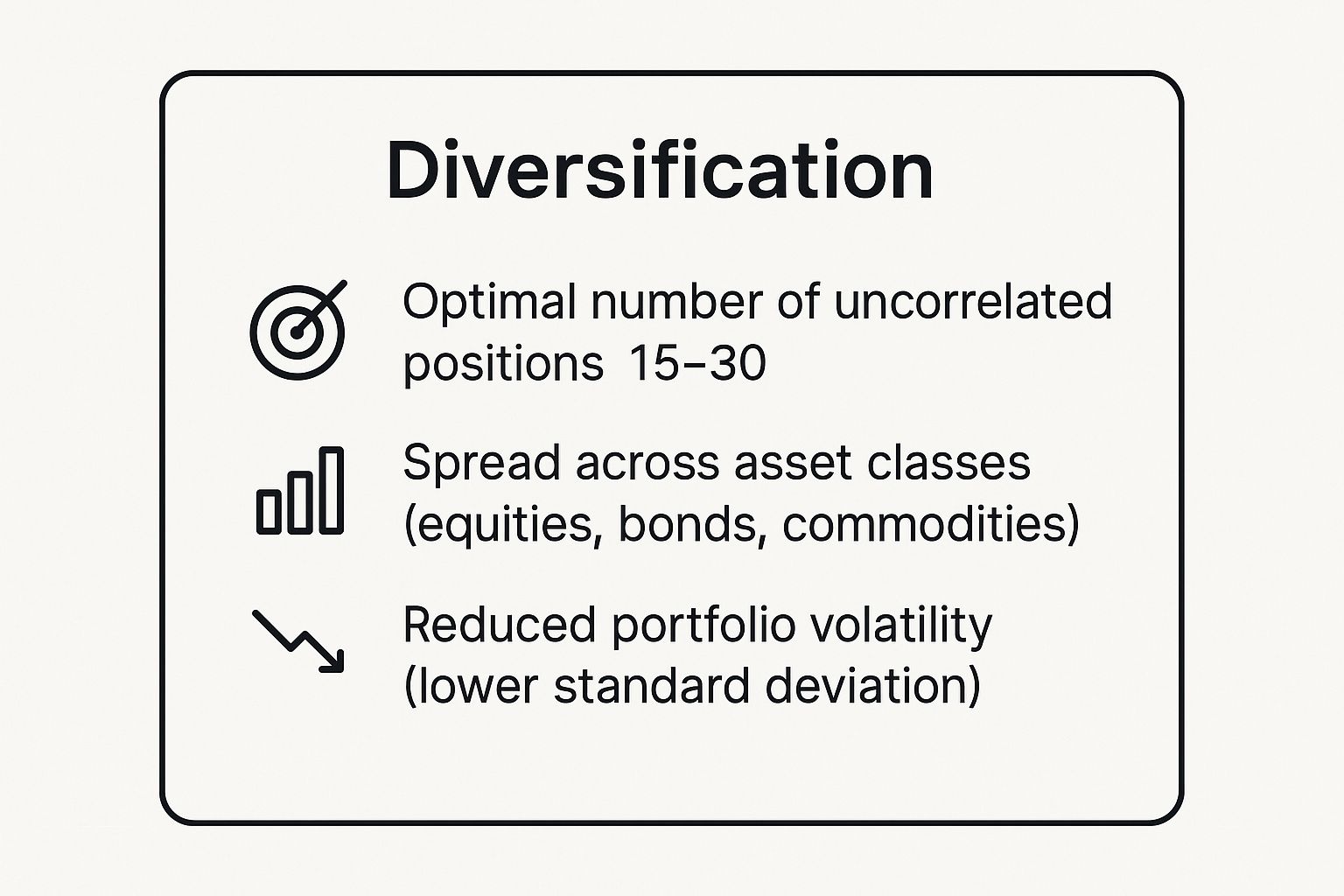
These key takeaways illustrate how diversification aims for a balanced portfolio that can lower overall volatility by spreading risk across different asset types. While it doesn't eliminate risk entirely, it is a powerful tool for managing it.
Key Insight: The true power of diversification is not just in owning different things, but in owning things that will perform differently under various market conditions. True diversification is about managing correlations, not just collecting assets. Monitor how your positions move together, especially during market stress, as correlations can often increase when it matters most.
4. Risk-Reward Ratio Analysis
Risk-reward ratio analysis is a foundational pillar of successful trading, ensuring your winning trades are meaningful enough to cover your losses and generate a profit over time. It’s a simple yet powerful calculation that compares the potential profit of a trade against its potential loss. This forward-looking assessment forces you to be selective, only taking trades where the upside potential sufficiently justifies the capital you are risking.
This principle is a common thread among disciplined traders. The legendary Turtle Traders, famously taught by Richard Dennis, were trained to seek trades with at least a 3:1 risk-reward ratio. Similarly, renowned swing trader Linda Raschke often targets a minimum 2:1 ratio for her setups. By systematically filtering for favorable ratios, these traders build a positive mathematical expectancy into their strategies, a core component of professional trading risk management techniques.
How to Implement Risk-Reward Ratio Analysis
The goal is to ensure that your potential reward is a multiple of your potential risk. A commonly accepted minimum is a 2:1 ratio, meaning for every $1 you risk, you aim to make at least $2.
Here’s the straightforward calculation:
- Calculate Your Potential Risk: The distance from your entry price to your stop-loss price.
- Calculate Your Potential Reward: The distance from your entry price to your profit target, which should be based on a logical technical level like a resistance zone or a Fibonacci extension.
- Determine the Ratio: Potential Reward / Potential Risk.
For example, imagine you want to buy a currency pair at 1.1200. You place your stop-loss at 1.1150 (a 50-pip risk) and set your profit target at 1.1300 (a 100-pip reward). The risk-reward ratio would be 100 pips / 50 pips = 2. This means you have a 2:1 ratio, which meets the minimum standard for a high-quality trade setup. This discipline is not just technical; understanding its importance is key to developing a resilient trading psychology.
Key Insight: A favorable risk-reward ratio acts as a buffer for your win rate. You don't need to be right most of the time to be profitable. With a 3:1 ratio, you only need to win more than 25% of your trades to break even (before costs), allowing you to make money even if you are wrong more often than you are right.
5. Portfolio Heat Management
Portfolio heat management is an advanced risk control technique that goes beyond single-trade risk to monitor the total, aggregate risk across all your open positions simultaneously. While position sizing controls the damage from one trade, portfolio heat ensures that the combined risk of all active trades doesn't exceed a predetermined threshold, preventing a "death by a thousand cuts" scenario where multiple small losses create a catastrophic portfolio-wide drawdown.
This institutional-grade approach is a cornerstone of sophisticated trading risk management techniques, moving the focus from individual trade outcomes to the overall health and stability of your entire trading book. Esteemed quantitative firms like Renaissance Technologies and Citadel employ real-time portfolio heat monitoring as a core defense mechanism. The concept, also championed by trading coach Van K. Tharp, asks a crucial question: "What is my total correlated risk exposure at this very moment?"
How to Implement Portfolio Heat Management
The central idea is to calculate and cap your total "risk on" as a percentage of your capital. This is your portfolio's "heat level." A common institutional limit is keeping total portfolio heat below 8-10% of your account equity.
Here’s a simple way to track it:
- Calculate Individual Trade Risk: For each open position, you already know the risk amount (e.g., 1% of your $10,000 account is $100).
- Sum All Active Risks: Add up the risk amounts for all your open trades. If you have five open trades, each with $100 at risk, your total portfolio heat is $500.
- Monitor the Heat Level: Calculate this sum as a percentage of your total capital. In this case, $500 is 5% of your $10,000 account, which is a manageable heat level. If you were to add another three trades, your heat would rise to $800, or 8%, approaching your pre-set limit.
To manage this effectively, use correlation analysis to avoid concentrating risk in highly correlated assets (e.g., being long on multiple major oil stocks simultaneously). When your portfolio heat approaches its maximum limit, you must either close some positions or significantly reduce the size of any new trades you take on. This proactive adjustment prevents over-exposure, especially during volatile market conditions.
Key Insight: Portfolio heat management acts as a circuit breaker for your entire trading operation. It forces you to think like a true risk manager, ensuring that a series of statistically likely losses occurring in a short period cannot jeopardize your long-term viability in the market.
6. Volatility Adjustment Techniques
Markets are not static; their riskiness ebbs and flows. Volatility adjustment techniques are advanced trading risk management techniques that dynamically adapt your strategy to current market conditions. Instead of using a fixed risk parameter, you modify your position size and stop-loss levels based on whether the market is calm or turbulent, ensuring your true risk exposure remains constant over time.
This approach acknowledges that a fixed 50-pip stop-loss carries far more risk in a volatile market than in a quiet one. The legendary Turtle Traders, a group of novice traders taught by Richard Dennis who went on to earn hundreds of millions, famously used the Average True Range (ATR) to normalize their risk. This allowed them to trade a wide variety of markets, from sleepy grains to wild currencies, with a consistent risk management framework. Quantitative funds and risk parity strategies have since perfected this concept.
How to Implement Volatility Adjustment
The most common tool for this is the Average True Range (ATR), which measures the average trading range over a specific period. It is a standard indicator available in your MT4 platform.
Here’s a practical way to apply it:
- Determine Volatility-Adjusted Stop-Loss: Instead of a fixed pip value, set your stop-loss as a multiple of the current ATR. For example, a 2x ATR stop-loss. If the 14-day ATR on EUR/USD is 70 pips, your stop-loss would be 140 pips from your entry.
- Calculate Position Size: Use this new, dynamic stop-loss distance to calculate your position size using the 1% rule. As volatility (ATR) increases, your stop-loss distance widens, which automatically reduces your position size to keep the dollar risk constant.
- Monitor Market-Wide Volatility: Keep an eye on the VIX (Volatility Index) to gauge overall market fear. When the VIX is high, you might consider reducing your overall risk percentage (e.g., from 1% to 0.5% per trade) for an added layer of defense.
Key Insight: By adjusting for volatility, you stop confusing price movement with risk. This technique ensures your risk per trade is based on the market's actual behavior, not an arbitrary number. It helps you stay in trades during noisy periods without getting stopped out prematurely, a cornerstone of robust trading risk management techniques.
7. Maximum Drawdown Limits
Maximum drawdown limits are one of the most critical trading risk management techniques for capital preservation. This technique establishes a predetermined point of maximum loss from an account's peak value, at which all trading activity is halted or significantly reduced. It acts as a circuit breaker, preventing the emotional and financial spiral that often accompanies a severe losing streak and ensures a trader can survive to trade another day.
This concept is a cornerstone of professional trading. While the infamous hedge fund Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM) ignored drawdown limits and collapsed in 1998, countless proprietary trading firms and successful traders build their entire risk framework around this rule. Legendary trader Victor Sperandeo, known as "Trader Vic," is a vocal advocate for a strict maximum drawdown rule, arguing that preserving capital during adverse periods is paramount to long-term success. It forces a trader to stop, reassess their strategy, and wait for better market conditions rather than trying to "win back" losses.
How to Implement Maximum Drawdown Limits
The key is to set your limit before you experience a drawdown, when you are thinking rationally. This limit is typically measured on a peak-to-trough basis, meaning from the highest point your account has reached.
Here’s a practical approach:
- Set a Hard Stop: Define an absolute maximum drawdown percentage that you will not breach. For most retail traders, a 15-20% limit is a standard and effective range.
- Establish Graduated Responses: Don't wait until you hit your maximum limit. Create a tiered system. For example, at a 10% drawdown, you might reduce your position size by 50%. At a 15% drawdown, you might stop trading for a week. At 20%, you stop trading entirely for a month and perform a full strategy review.
- Track Your Performance Diligently: This technique is only effective if you monitor your account equity curve. Consistently using tools to track trading performance is essential for identifying when you are approaching your predefined limits. For more information, you can learn about how to track your trading performance.
Key Insight: A maximum drawdown limit is not a sign of weakness; it is a mark of professional discipline. It separates your trading ego from your account balance, forcing an objective, pre-planned response to a losing streak and preventing a manageable downturn from becoming a career-ending disaster.
Risk Management Techniques Comparison
| Technique | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position Sizing | Moderate 🔄 | Low to Moderate ⚡ | Consistent risk control, capital preservation 📊 | All trading timeframes, risk management foundation 💡 | Prevents large losses, optimizes risk-reward ⭐ |
| Stop-Loss Orders | Low 🔄 | Low ⚡ | Automatic loss limitation, stress reduction 📊 | Traders seeking automated exit, emotional control 💡 | Limits losses, removes emotion, always active ⭐ |
| Diversification | Moderate 🔄 | Moderate to High ⚡ | Reduced portfolio risk, smoother returns 📊 | Portfolio management, reducing systemic risk 💡 | Lowers volatility, multiple profit streams ⭐ |
| Risk-Reward Ratio Analysis | Low to Moderate 🔄 | Low ⚡ | Improved trade selection, positive expectancy 📊 | Trade evaluation, ensuring profitability over time 💡 | Mathematical edge, discipline in trading ⭐ |
| Portfolio Heat Management | High 🔄 | High ⚡ | Controls total portfolio risk, avoids big drawdowns 📊 | Advanced traders, institutional risk control 💡 | Accounts for correlations, professional risk level ⭐ |
| Volatility Adjustment Tech | Moderate to High 🔄 | Moderate to High ⚡ | Consistent risk across market states 📊 | Volatile markets, dynamic risk management 💡 | Adjusts risk dynamically, reduces whipsaws ⭐ |
| Maximum Drawdown Limits | Moderate 🔄 | Low to Moderate ⚡ | Capital preservation during losing streaks 📊 | Risk control during drawdowns, maintaining discipline 💡 | Protects capital, enforces risk limits ⭐ |
Final Thoughts
The journey through the world of trading is often perceived as a quest for the perfect entry or exit signal. However, as we have detailed, the true foundation of sustainable success is not found in a mystical indicator but in the disciplined application of robust trading risk management techniques. The methods discussed, from the granular precision of Position Sizing and Stop-Loss Orders to the strategic oversight of Portfolio Heat Management and Maximum Drawdown Limits, are not merely suggestions; they are the architectural pillars that support a lasting trading career.
Ignoring these principles is akin to building a skyscraper on a foundation of sand. A single unexpected market tremor, a volatile news event, or a period of emotional decision-making can bring the entire structure crashing down. Conversely, mastering these techniques transforms trading from a high-stakes gamble into a calculated business endeavor. It shifts your focus from chasing fleeting profits to systematically protecting your capital, ensuring you have the resources to trade another day, another week, and another year.
Synthesizing Your Risk Management Framework
The true power of these concepts emerges when they are integrated into a cohesive, personal framework. It’s not about picking one technique over another but about understanding how they interlink and support each other.
- Position Sizing and the Risk-Reward Ratio work hand-in-hand to define the parameters of every single trade before you even enter the market.
- Stop-Loss Orders act as your automated, non-negotiable line of defense, executing your plan without emotional interference.
- Diversification and Volatility Adjustments provide a macro-level defense, protecting your entire portfolio from concentrated, asset-specific shocks or broad market turbulence.
- Maximum Drawdown Limits serve as your ultimate circuit breaker, forcing a strategic pause and reassessment when performance deviates significantly from your expectations.
Think of this as building a multi-layered shield. Each technique is a different layer, and together, they provide comprehensive protection that allows you to operate with confidence, even in the most uncertain market conditions. The goal is to make risk management an unconscious, systematic habit, as reflexive as checking your mirrors before changing lanes.
Your Path Forward
The path to mastery begins now. Don't just read about these concepts; implement them. Start with a demo account if you must, but begin the process of defining your rules. Calculate your risk per trade, set your stop-losses with intention, and analyze your portfolio's overall heat. Track your drawdown and respect the limits you set for yourself. This deliberate practice is what separates amateur speculators from professional traders. By embracing these essential trading risk management techniques, you are not just learning to trade; you are learning how to build a resilient, long-term business in the financial markets.
Ready to implement these professional risk management strategies with unparalleled precision? OTC Charts MT4 provides the real-time data and advanced charting tools you need to analyze volatility, set precise stop-loss levels, and manage your portfolio directly within the industry-standard MT4 platform. Elevate your trading by visiting OTC Charts MT4 and integrating professional-grade analytics into your workflow today.


